Capacitance also depends on the dielectric constant of the dielectric material separating the plates.
The standard units of Capacitance;
farad: F
microfarad: µF (1 µF = 10-6 F)
nanofarad: nF (1 nF = 10-9 F)
picofarad: pF (1 pF = 10-12 F)
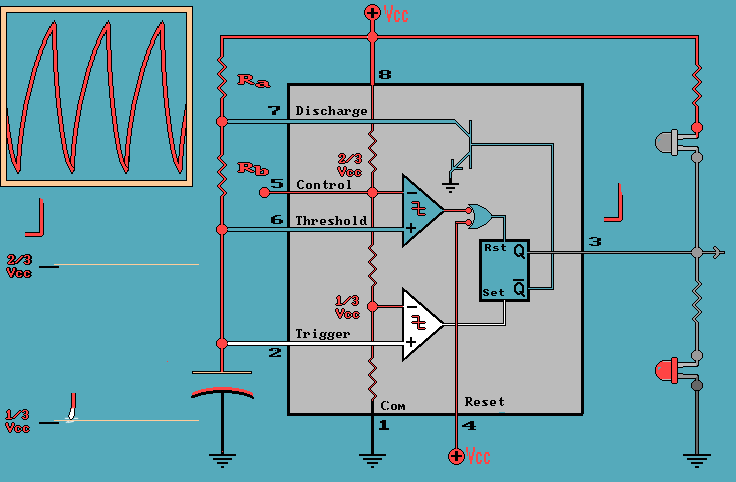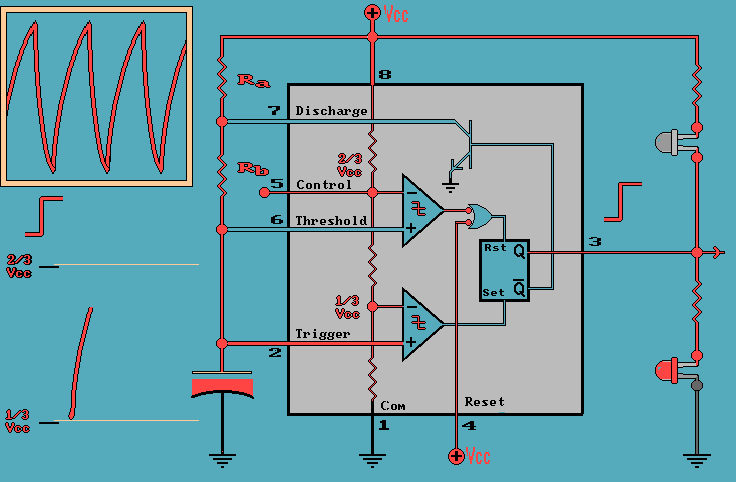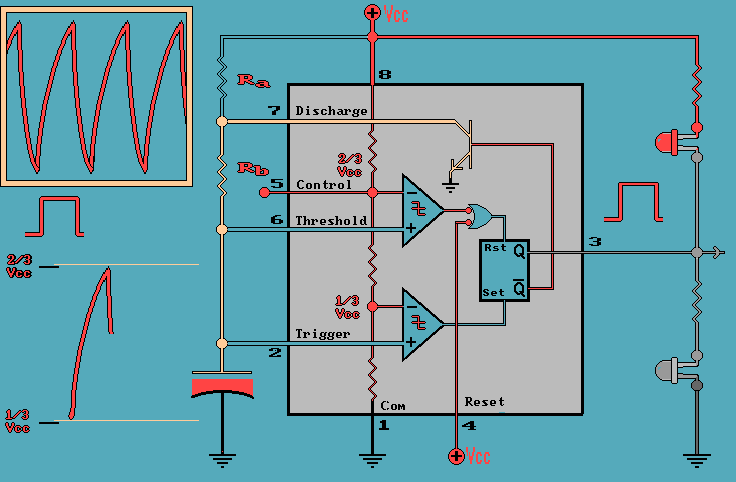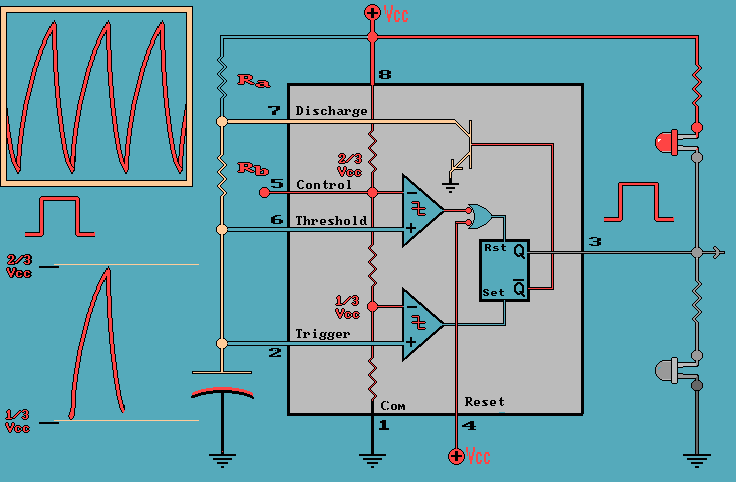
Capacitor as a Timing Element
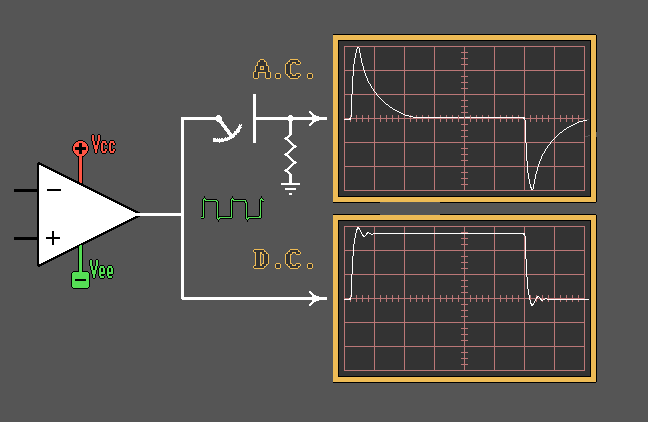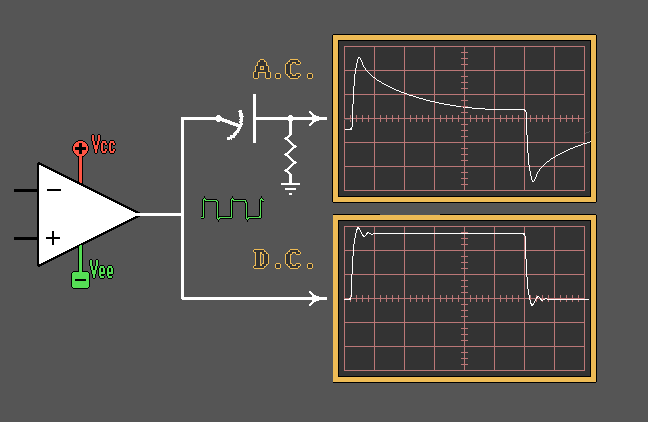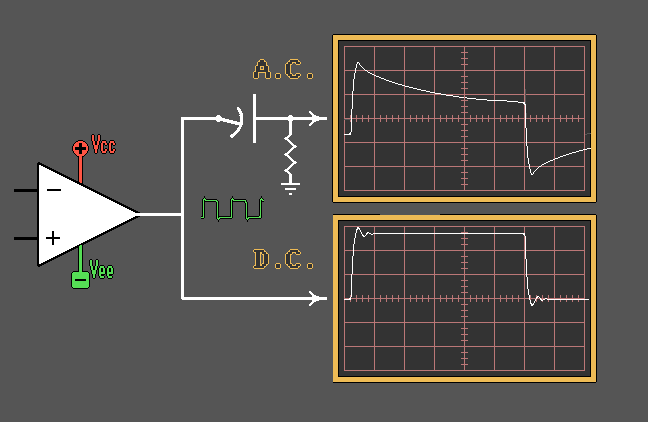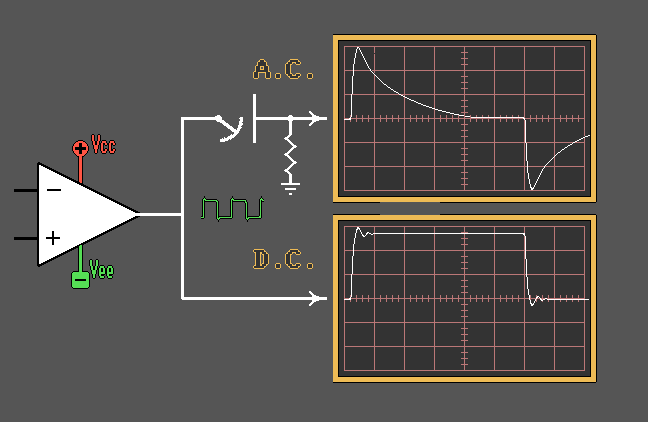
Capacitor as a Coupling
Element
Capacitor as a Filtering Element
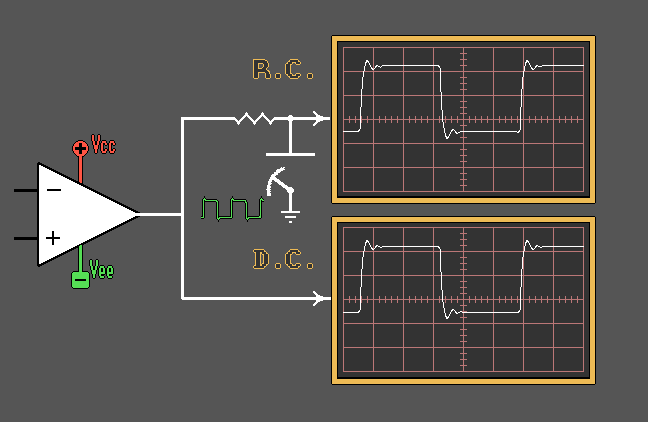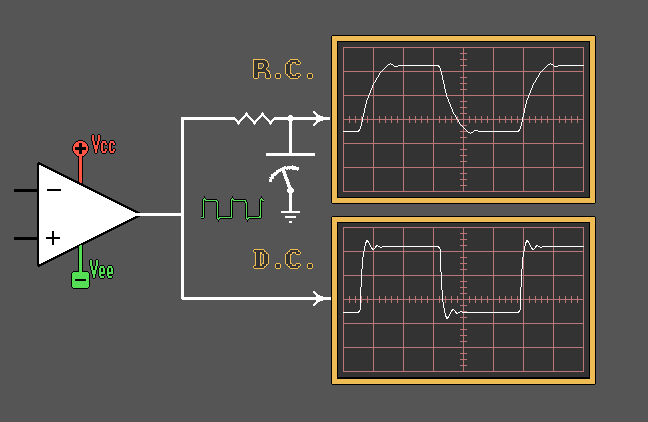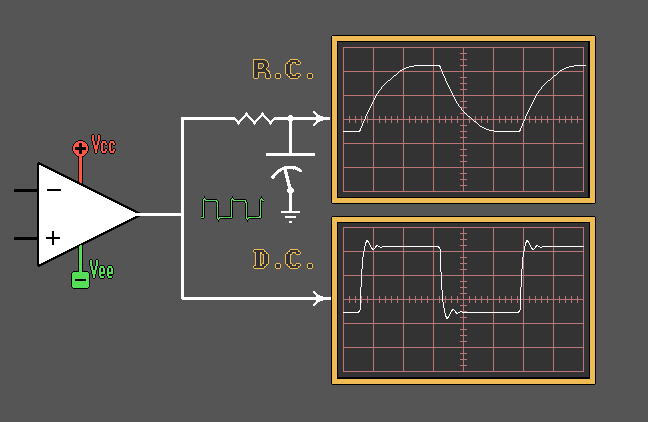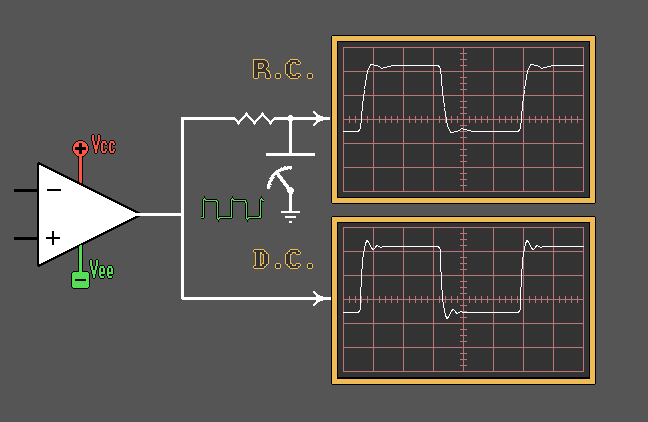
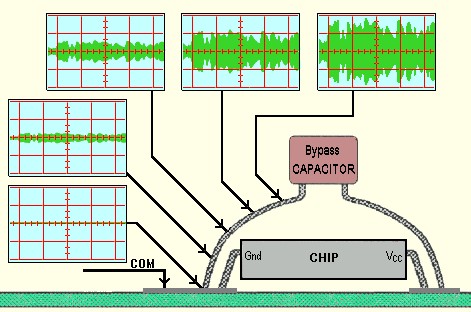
Capacitors as Power Supply "Bypassing"
Elements
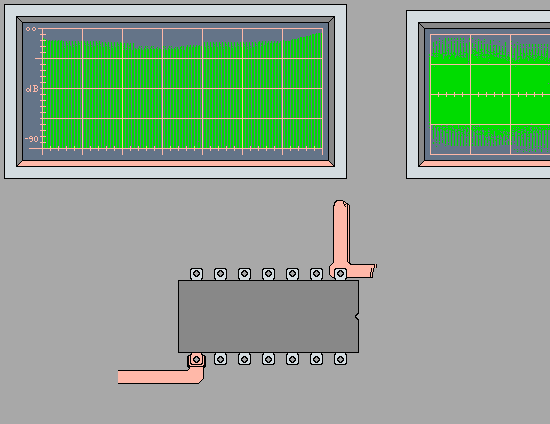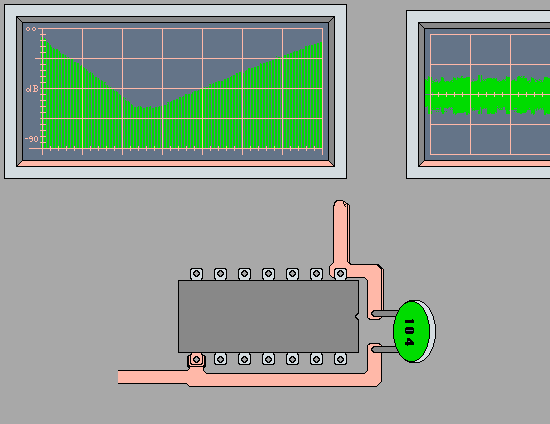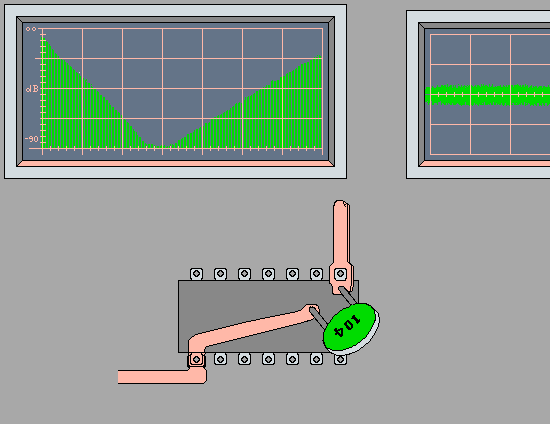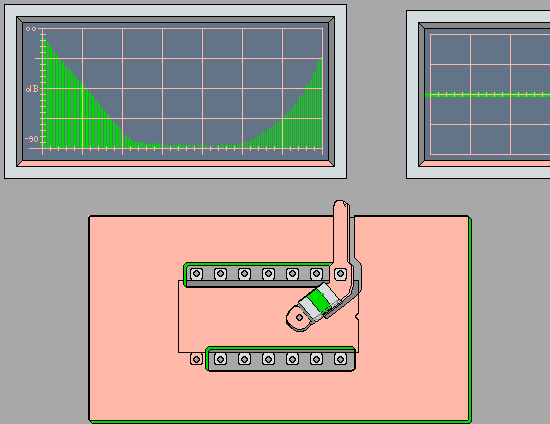
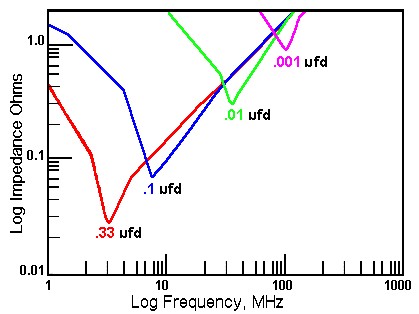
Bypass Capacitors' Minimum Impedance at
Self Resonance
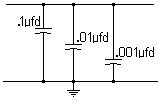
Paralleling Bypass Capacitors for Maximum
Effectiveness